The womb is a incredible organ, primarily found in feminine mammals, and plays a essential role in reproduction. It's a muscular organ located in the pelvis, responsible for nurturing a growing baby during pregnancy. Beyond childbirth, the matrix also sheds its endometrium during the period, which is a natural event in a woman's life. This shape is typically rounded, and the organ can stretch considerably to accommodate a full-term baby.
Learning About These Organs
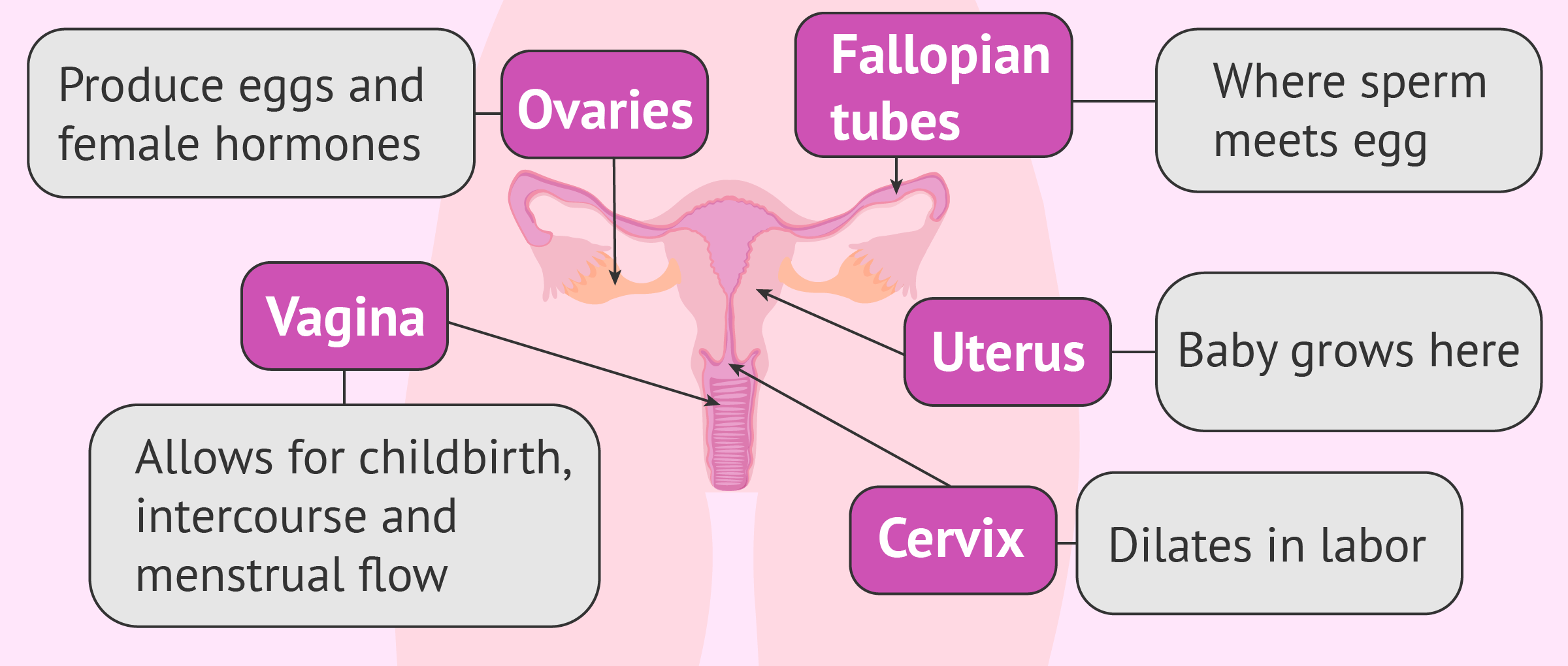
The female gonads are crucial components of the female reproductive framework, primarily accountable for producing eggs and hormones. Typically, females have two gonads, located on either side of the uterus. They undertake a significant part throughout a woman's life, commencing with development during fetal stages and persisting through menstruation and potentially into this life phase. Their intricate functions are closely connected with the overall health and wellness of a woman.
Understanding Salpingian {Tubes
Fallopian ducts are vital structures of the woman's procreative apparatus, playing a significant part in reproduction. They extend from the uterus to the ovaries, acting as a pathway for the ovum to travel from the testicle to the uterus. Often, conception occurs within the isthmus, a defined area of the fallopian channel. Additionally, disease or a obstruction of these ducts can substantially influence reproduction.
Keywords: vagina, vulva, anatomy, health, female, reproductive, intimate, hygiene, disorders, sexually transmitted infections, lubrication, childbirth, menstruation, pelvic floor, estrogen, pH balance, yeast infection, bacterial vaginosis, pelvic pain.
The Female Intimate Opening
The birth canal is a remarkable part of the female internal structure, often confused with the vulva. It plays a critical role in childbirth, menstruation, and intimate well-being. Proper care is essential for preventing problems like fungal infections, bacterial vaginosis, and addressing discomfort. Factors such as hormonal levels, pH balance and adequate lubrication significantly impact the woman's function. Awareness of STIs and their potential impact on the female region is also extremely important for overall personal well-being. The strength of the pelvic floor is also important for recovery.
A Vulva
The outer female reproductive structure encompasses the visible parts of the female’s genital area outside of the body. It's a complex structure with many functions, including shielding the delicate parts and serving a function in reproductive activity. Understanding its structure is important for overall wellness and childbearing understanding. This encompasses the labia, glans, and the area which contains the urinary port and birth opening.
A Cervical Canal
The cervix, a important part of the female anatomy, functions as a passage between the uterus and the vagina. Typically, it is a tight channel, about a few centimeters long, and has a significant role in periodical cycles and childbirth. In pregnancy, the uterine neck remains closed to safeguard the growing fetus, and then dilates significantly to allow delivery. The health of this organ is necessary for reproductive overall health.
Exploring the Labia Majora
The labia majora are an pair of significant skin structures that are part of the external genital system. Often, they mirror the pubic mound, being made up of fatty substance and shrouded by pubic fur, although this may vary widely among people. Playing as a important safeguarding shield, these aid to shield the inner sensitive elements within the genital area, while these contribute to the overall form and role of a woman's anatomy.
Exploring These Minora
These inner lips are an pair of flexible folds that make up flesh located just inside the labia. These folds differ significantly in size, appearance, and shade between women, and appear more pigmented than the nearby skin. Although this region lack a clear purpose regarding reproduction, these folds important for shielding of delicate inner structures. Variations in their size or consistency may sometimes indicate the medical issue, so it's important to obtain expert guidance if certain worries develop.
Exploring A Clitoris
Numerous people find the clitoris, a small organ situated at the front of the female genitalia, to be an crucial area regarding sexual enjoyment. Unlike other genital organs, it lacks a direct function in reproduction; its only role is related to sexual feeling. The structure is remarkably sensitive, comprising numerous of sensory endings, making it to deliver intense sensations. More investigation continues to expand our understanding of this sophisticated anatomy and function.
- The is often called the final erotic zone.
- Some believe understanding of the clitoris is often liberating.
Understanding Bartholin's Glands
Found on both side of the vaginal opening, Bartholin's glands|glands|structures are a usually small role in female reproductive health. Usually, they release a small amount of fluid|lubrication|moisture that supports with vaginal lubrication during sexual activity. Occasionally, these glands|ducts|tubes can be obstructed|clogged|swollen, leading to a painful lump|swelling|mass and difficulty with walking. A condition, known as a Bartholin's lump, often necessitates doctor's attention.
Okay, here's the article paragraph adhering to your strict spintax and HTML requirements, focusing on Skene's Glands.
Understanding Accessory {Glands
Skene's ducts, also known as paraurethral ducts, are accessory structures located near the urethra on the woman's anatomy. These glands play a role similarly to the male prostate structure, producing a liquid that contributes lubrication and defense of the urethra. Despite these function isn't completely known, research indicates these might play a role in woman's reproductive function. Certain individuals may have sensitive problems related to the structures, prompting further investigation. In conclusion, Skene’s ducts represent an critical but often overlooked component of female internal structure.
Keywords: hymen, virginity, anatomy, female, membrane, health, misconception, folklore, cultural, biology, medical, intact, rupture, bleeding, hymenal, tissue, perception, history, examination, psychology.
The Hymen Overview
The hymen is a slight fold of skin located near the uterus in women. Sometimes associated with chastity in cultural contexts, it's crucially a component of female biology. It’s important to appreciate that the hymeneal membrane isn’t always unaffected, and its presence or lack doesn’t definitively reveal virginity. Numerous activities, including physical activity, tampon use, or even intense sneezing, can cause a rupture of the hymen. The commonly-debated bleeding sometimes associated with female structure break is not but isn’t always present. Clinical professionals may conduct an examination of the hymen, but its appearance shouldn’t be considered as a sole measure of reproductive background. There are many misconceptions surrounding the hymeneal tissue and it's vital to separate scientific information from cultural myths and emotional beliefs.
Okay, here's an article paragraph on "Perineum" adhering to your incredibly specific instructions.
Understanding the Perineum
The perineal region is a fascia-covered region situated directly below the anus and the scrotum in males. The structure functions a critical part in several bodily functions, like stabilizing the lower structures and assisting in tactile feedback. Moreover, it undergoes considerable elongation during vaginal delivery in females, that can cause temporary pain. Knowing about its structure is thus essential for clinical experts.
Learning About Your Body's Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor is a set of tissues that hold your bladder and have a vital role in general health. It's often overlooked, but improving your pelvic floor can benefit everything from urinary control to stability. Problems like incontinence or pelvic pain can sometimes are alleviated with specific training. It's beneficial learning about your pelvic area and how to maintain them healthy throughout your time.
The Vaginal Canal
The female canal, also known as the introitus, is a muscular passage extending from the external genitalia to the uterine neck. It serves as the primary route for monthly flow, copulatory intercourse, and labor and delivery. This flexible structure is lined with epithelium and possesses distinctive folds, called longitudinal folds, which allow it to dilate considerably. Its depth varies among women, but typically measures around 7-10 centimeters in normal state. Maintenance of the vaginal canal is crucial for reproductive health and well-being.
This Internal Layer (Endometrium)
The internal layer is a remarkably dynamic tissue that fulfills a crucial role in female reproductive capacity. This inner membrane of the uterus is discarded during menstruation if pregnancy doesn’t occur , and it thickens each month in readiness for a potential implantation of a fertilized egg . It’s made up of glandular and stroma cells, creating a specific environment that constantly adapts throughout the reproductive cycle. Furthermore , the endometrial depth and composition are significantly affected by chemical messengers , primarily estrogen and gestogen .
Exploring Ovarian Follicles
Female follicles are essential structures within the female reproductive organ, playing a central role in the growth of ova and the maintenance of the period. Each ovary initially contains a large number of primordial follicles, which are immature sacs containing immature eggs. Throughout a woman's reproductive life, these follicles mature through different stages, some undergoing dominant follicle selection, others remaining in a dormant state. The course of follicle development involves intricate interactions between hormones, including reproductive hormones and luteinizing hormone, which guide the stages leading to reproduction.
Exploring Estrogen Receptors
Estrogen receptors are intracellular proteins found within multiple cell kinds throughout the organism. These important elements act as gatekeepers, binding to estrogen agents and subsequently causing a cascade of cellular events. Basically, when an oestrogen agent binds to a receptor, it promotes a shape alteration that leads to altered gene transcription, influencing many activities, such as growth, breeding, and general condition. The presence and density of these binders can change significantly across tissues, accounting for the varied effects of estrogen in the human organism.
Pregnancy Binders
Progesterone receptors, often abbreviated as PRs, are intracellular proteins that mediate the actions of progesterone, a vital steroid chemical. These proteins are part of the nuclear receptor superfamily and, upon binding with progesterone, undergo a conformational shift leading to translocation to the nucleus and subsequent control of gene expression. Two major types, PR-A and PR-B, are present due to alternative processing of the mRNA, each exhibiting subtly different influencing properties and tissue location. Their function is essential in the support of gestation, the development of the lactating glands, and the regulation of the reproductive cycle in women. Dysregulation of estrous receptor signaling has been implicated in a range of fertility disorders.
Keywords: reproductive system, male reproductive system, female reproductive system, fertilization, hormones, ovaries, testes, uterus, sperm, egg, menstruation, puberty, pregnancy, contraception
A Reproductive System
The human reproductive system is a complex network of organs responsible for continuation of the species. It generally separates into the male reproductive system and the female reproductive system, each with distinct functions. In males, the testes produce sperm, while in females, the ovaries release eggs. Fertilization, the combination of a sperm and an egg, can lead to pregnancy, a incredible period of development . Hormones, like estrogen and testosterone, play a critical role in regulating development during puberty and throughout reproductive life. Menstruation is a recurring process in females, and contraception methods get more info are obtainable to avoid unintended pregnancies. This amazing system is crucial to the perpetuation of our kind .